By DENNIS WASZAK Jr. AP Pro Football Writer
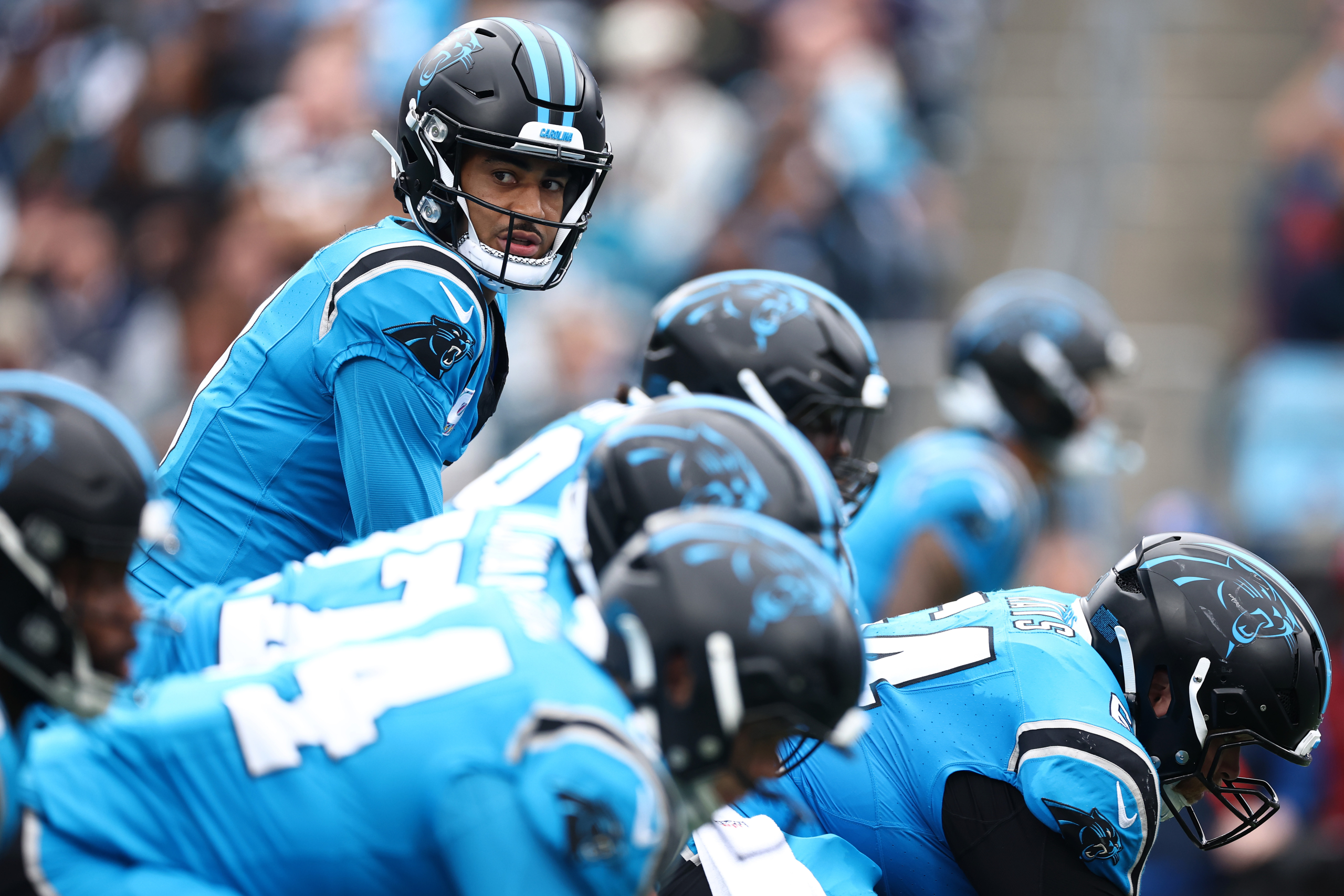
EAST RUTHERFORD, N.J. (AP) — Bryce Young’s arrival in Carolina came with huge expectations.
He was the No. 1 pick in the 2023 NFL draft, hoped by the Panthers to be the quarterback to help lead the franchise back to respectability, the playoffs and perhaps someday much more.
Well, small steps first.
The Panthers (3-3) head to New York to play the winless Jets (0-6) on Sunday and look to win three straight games for the first time with Young as their starting quarterback. They also haven’t had a .500 record this deep into a season since they were 5-5 in Cam Newton’s second stint with the team in 2021.
“So proud of this group that just continues to fight and scratch and claw and just get it done,” coach Dave Canales said after the Panthers’ 30-27 win over the Dallas Cowboys last Sunday.
There’s a feeling among the players that things are different now for a team that has a franchise-worst seven-year playoff drought, tied with Atlanta for the NFL’s second-longest active skid behind only the Jets. Young agreed with guard Damien Lewis, who posted on social media that he feels a culture change is underway in Carolina.
“I feel like we’re definitely continuing to build and grow in the right direction,” Young said. “I’m embracing the culture, embracing the ownership and all the little things, and I think us being able to come into our own, it’s been great. It’s been great to be a part of, and it’s been great to be a leader through it.
“So, you know, there’s still work to do. Still so much for us to build off of.”
The Panthers will have to solve their road woes if they hope to keep things rolling. Carolina is 0-3 away from Bank of America Stadium and been outscored 95-45 in those games.
Meanwhile, the Jets are 0-6 for the third time in franchise history and will try to avoid joining the 1996 and 2020 squads as the only teams to drop their first seven games.
Aaron Glenn is the first Jets coach to begin his tenure with six losses, and fans already frustrated with the team’s 14-year playoff drought are already losing patience.
“I understand how it looks on the outside, and the thing is, I told you guys and I told the fans, man, do not let go of the rope,” Glenn said. “The thing I know we’re doing is we’re trying to build a solid foundation so we can consistently try to win.”
Split backfield?
Panthers running back Rico Dowdle has been dominant the past two weeks, racking up 389 yards on the ground and 473 yards from scrimmage — both franchise records for a two-game span.
But with regular starter Chuba Hubbard set to return this week from a calf injury, Dowdle could get fewer reps. Canales has remained quiet on his plans on who’ll receive the bulk of carries, but insisted Dowdle will remain part of the mix.
“I think he’s earned everything that he’s done in the last two weeks,” Canales said of Dowdle. “He’s earned the right to help this team, and he will. We’ll find a way to do that. How we do that specifically, I don’t wanna really share those details of it.”
Things can only go up
Justin Fields went 9 of 17 for just 45 yards and was sacked nine times, a result of holding onto the ball too long at times, in New York’s 13-11 loss to Denver in London last Sunday. The Jets also finished with a franchise-worst minus-10 net yards passing.
Still, Glenn is sticking with Fields as his starter, looking for the quarterback and coordinator Tanner Engstrand’s struggling unit to bounce back.
“I think I’ll just learn from my mistakes from last game,” Fields said, “and definitely play better this week, for sure.”
Wilson watch
Fields and the offense could have an even tougher time getting on track if star wide receiver Garrett Wilson is sidelined.
Wilson is dealing with a knee injury that kept him out of practice early in the week and Glenn said the Jets would see how he’d progress. The fourth-year receiver leads New York with 36 catches for 395 yards and four touchdowns.
But that’s not all: No. 2 wide receiver Josh Reynolds also might not play because of a hip ailment. That could leave the Jets with Allen Lazard, Tyler Johnson and rookie Arian Smith as the only healthy wide receivers on the active roster.
Coker’s return
Panthers wide receiver Jalen Coker, who carved a niche last season as an undrafted rookie with 32 receptions for 478 yards and two touchdowns, is set to make his season debut as the team’s slot receiver.
Coker missed the first six games with a quadriceps injury suffered leading up to the season opener, which he called “really unfortunate timing.”
The Panthers have been careful to make sure Coker is completely healed and that his conditioning is at a point where he can play the entire game and be a contributor and not be on a snap count.
Edge rushers needed
The Panthers lost outside linebacker Patrick Jones II, one of their top pass rushers, for the season with a lower back injury this week.
Carolina is expected to turn to rookies Nic Scourton and Princely Umanmielen, the team’s second- and third-round picks, to replace Jones. Both have shown promise, but are now expected to get expanded roles.
___
AP Sports Writer Steve Reed in Charlotte, North Carolina, contributed.